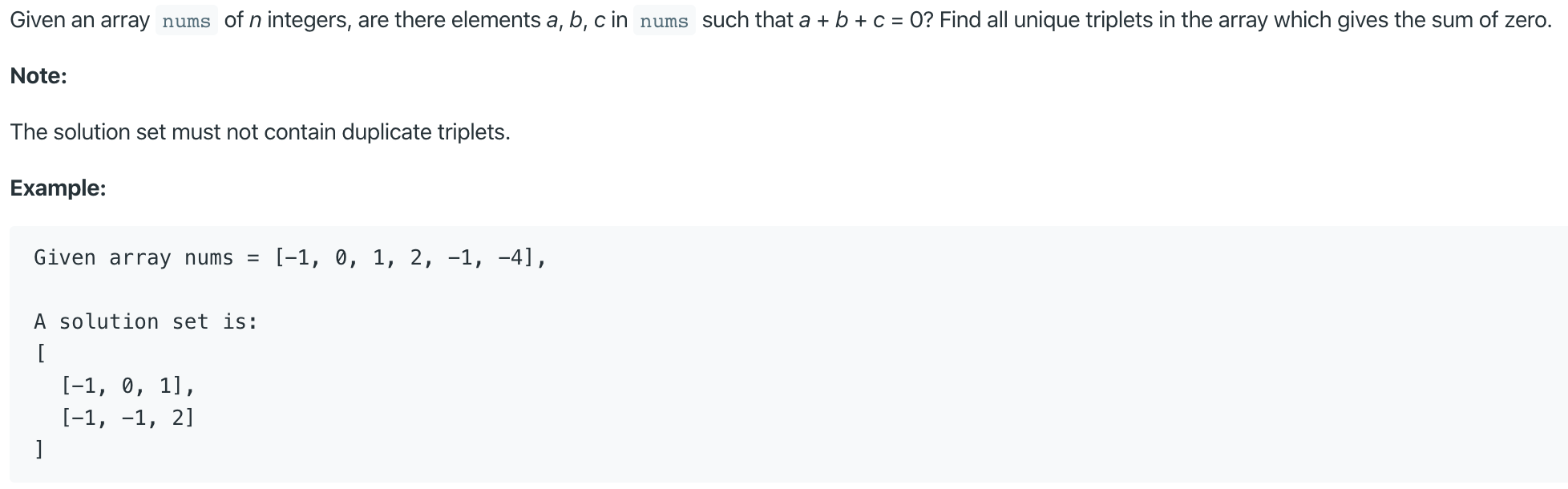
Three Sum
franklinqin0 ArrayTwo Pointers
# Solution
The brute force solution doesn't sort and takes 3 nested for loops for cubic time.
Sorting() was not a good practice in linear time two sum but should be used in this squared time problem.
# Vanilla Two Pointers
Sort and then use two pointers to search for satisfied result. Caveat is to look out for duplicates.
Complexity
time:
space:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
nums.sort()
for i in range(len(nums)-2):
# no need to continue searching b/c nums is sorted
if nums[i] > 0:
break
# i>0 s.t. i-1>=0
# continue if `curr == prev` to eliminate duplicates on smallest elt
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
continue
target = -nums[i]
left = i + 1
right = len(nums) - 1
while left < right:
if nums[left] + nums[right] == target:
res.append([nums[left], nums[i], nums[right]])
# if the current left/right is the same w/ the next, a duplicate would be returned
while left < right and nums[left] == nums[left+1]:
left += 1
while left < right and nums[right] == nums[right-1]:
right -= 1
# update left/right after eliminating duplicates
left += 1
right -= 1
elif nums[left] + nums[right] < target:
left += 1
else:
right -= 1
return res
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# Return a Set
Also sort and then use two pointers, but the difference is returning a set rather than list.
To eliminate duplicates, use tuple rather than list for HashSet res.
Complexity
time:
space:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = set()
n = len(nums)
nums.sort()
for i in range(n-2):
target = -nums[i]
left = i + 1
right = n - 1
while left < right:
# speed up a bit
if nums[i] > 0:
break
if nums[left] + nums[right] == target:
res.add((nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]))
left += 1
right -= 1
elif nums[left] + nums[right] < target:
left += 1
else:
right -= 1
return res
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22