Add Two Numbers II
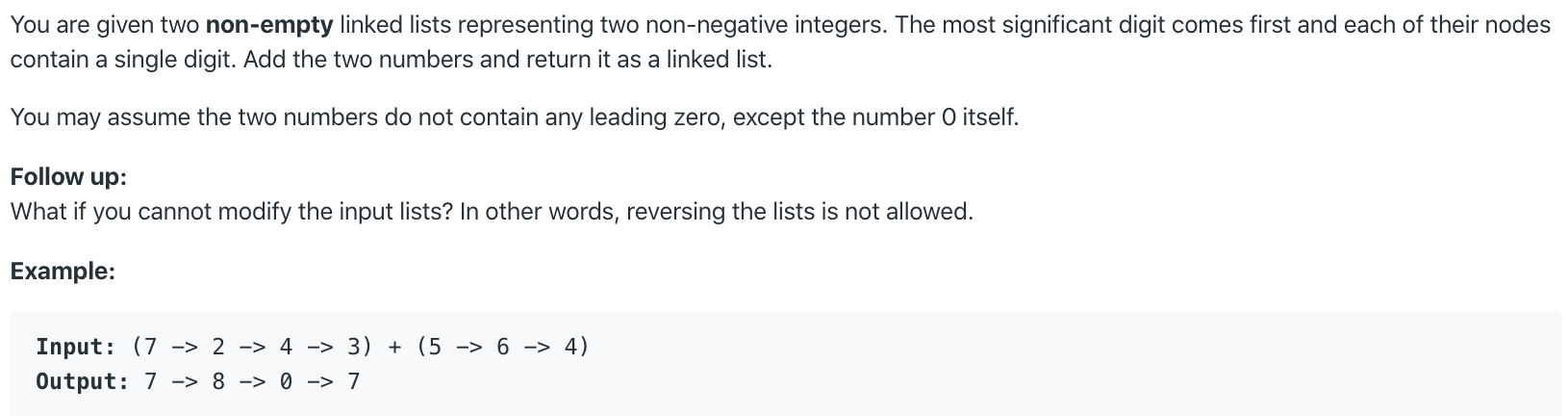
See the easier related problem Add Two Numbers.
# Solution
Let be the length of l1, and be the length of l2.
# Reverse Linked List & DIY ListNode Adder
Create a nested function reverseList(similar as in reverse linked list) to reverse the two input linked list and then construct a ListNode adder(similar as in add two numbers).
Complexity
time:
space:
where m is the number of nodes in l1 and n is the number of nodes in l2.
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
def reverseList(l: ListNode) -> ListNode:
prev = None
curr = l
# IMPT: reverse a singly linked list
while curr:
nxt = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = nxt
return prev
new_l1 = reverseList(l1)
new_l2 = reverseList(l2)
carry = 0
end = dummy = ListNode(0)
while new_l1 or new_l2 or carry:
if new_l1:
carry += new_l1.val
new_l1 = new_l1.next
if new_l2:
carry += new_l2.val
new_l2 = new_l2.next
end.next = ListNode(carry%10)
end = end.next
carry = carry//10
return reverseList(dummy.next)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# Follow Up
What if you cannot modify the input lists? In other words, reversing the lists is not allowed.
# Vanilla Addition
Complexity
time:
space:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# find the length of both lists
n1 = n2 = 0
curr1, curr2 = l1, l2
while curr1:
curr1 = curr1.next
n1 += 1
while curr2:
curr2 = curr2.next
n2 += 1
# parse both lists & sum the corresponding positions w/o taking carry into account
# 3->3->3 + 7->7 --> 3->10->10 --> 10->10->3
curr1, curr2 = l1, l2
head = None
while n1 > 0 and n2 > 0:
val = 0
if n1 >= n2:
val += curr1.val
curr1 = curr1.next
n1 -= 1
if n1 < n2:
val += curr2.val
curr2 = curr2.next
n2 -= 1
# update the result: add to front
curr = ListNode(val)
curr.next = head
head = curr
# take the carry into account to have all elements < 10
# 10->10->3 --> 0->1->4 --> 4->1->0
curr1, head = head, None
carry = 0
while curr1:
# current sum and carry
val = (curr1.val + carry) % 10
carry = (curr1.val + carry) // 10
# update the result: add to front
curr = ListNode(val)
curr.next = head
head = curr
# move to the next elements in the list
curr1 = curr1.next
# add the last carry
if carry:
curr = ListNode(carry)
curr.next = head
head = curr
return head
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
# Stack
Initialize two stacks for l1 and l2 respectively: s1 and s2. After appending, pop each stack, calculate the sum, and create the calculated sum as new head.
Complexity
time:
space: due to extra space of 2 stacks
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
s1 = []
s2 = []
while l1:
s1.append(l1.val)
l1 = l1.next
while l2:
s2.append(l2.val)
l2 = l2.next
carry = 0
head = None
while s1 or s2 or carry:
a = s1.pop() if s1 else 0
b = s2.pop() if s2 else 0
sum = a + b + carry
carry, sum = divmod(sum, 10)
curr = ListNode(sum)
curr.next = head
head = curr
return head
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# Recursion
The recursive function add_list is not easy to write(especially what vars to return). The idea is:
- get the difference in length of
l1andl2 - IMPT: recursively add two lists and return
headandnew_carry. Note thatdiffdecreases only whenln1is longer thanln2 - if there is a leftmost carry, make it head and return
Complexity
time:
space: (due to implicit stack space)
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
def get_len(l: ListNode) -> int:
length = 0
while l:
l = l.next
length += 1
return length
def add_lists(ln1: ListNode, ln2: ListNode, diff: int) -> (ListNode, int):
if ln1 is None and ln2 is None:
return None, 0
if diff > 0:
# currently ln1 is longer than ln2
# move the pointer at list1 to ln1.next, don't move the pointer at list2
next_node, carry = add_lists(ln1.next, ln2, diff-1)
carry += ln1.val
else:
next_node, carry = add_lists(ln1.next, ln2.next, diff)
carry += ln1.val + ln2.val
new_val, new_carry = carry%10, carry//10
head = ListNode(new_val)
head.next = next_node
return head, new_carry
l1_len, l2_len = get_len(l1), get_len(l2)
# always keep len(ln1) >= len(ln2)
if l1_len < l2_len:
l1_len, l2_len = l2_len, l1_len
l1, l2 = l2, l1
diff = l1_len - l2_len
head, carry = add_lists(l1, l2, diff)
# handle the leftmost carry
if carry:
c = ListNode(carry)
c.next = head
head = c
return head
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37