Kth Largest Element in an Array
franklinqin0 HeapQuick Select
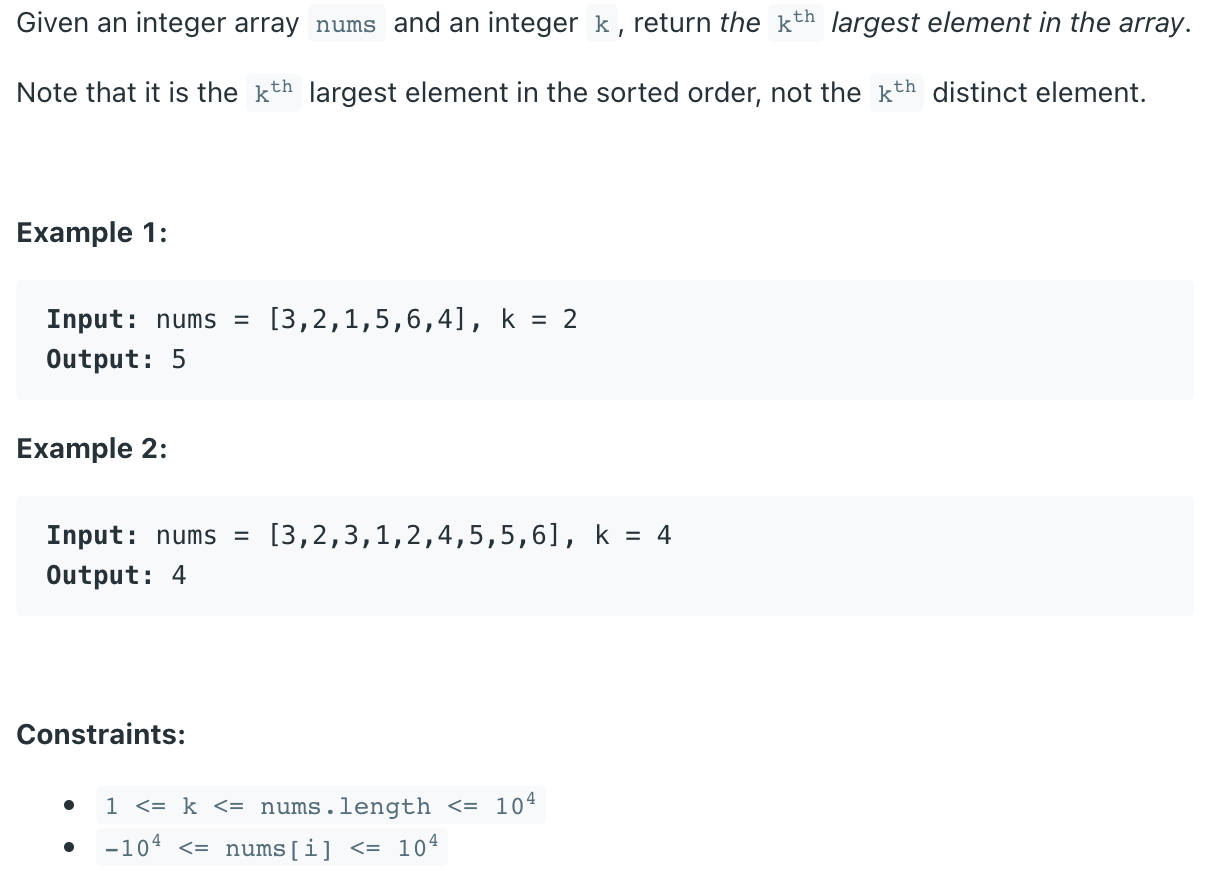
# Solution
Let be the length of the array.
# 1-liner Cheating
Use sorted:
def findKthLargest(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
n = len(nums)
return sorted(nums)[n-k]
1
2
3
2
3
Or use built-in heapq:
def findKthLargest(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
return heapq.nlargest(k, nums)[-1]
1
2
2
# Heap
Why does heappop work?
Because after iterating through all elements, the heap maintains exactly k elements. Since it's a min-heap, the smallest element in the heap is the k-th largest element in the original array.
Complexity
time:
space:
from heapq import heappush
def findKthLargest(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
n = len(nums)
heap = []
for i in range(n):
heappush(heap, nums[i])
if len(heap) > k:
heappop(heap)
return heappop(heap)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# Quick Select
Complexity
time: (worst case: )
space:
# Lomuto Partition
def findKthLargest(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
def partition(arr, left, right):
# move pivot to the end
pivot = arr[right]
store_idx = left
for i in range(left, right):
# move elt smaller than pivot to the left
if arr[i] < pivot:
arr[store_idx], arr[i] = arr[i], arr[store_idx]
store_idx += 1
arr[store_idx], arr[right] = arr[right], arr[store_idx]
return store_idx
def quickSelect(arr, left, right, k):
if left == right:
return arr[left]
pivot_idx = partition(arr, left, right)
if k == pivot_idx:
return arr[k]
if k < pivot_idx:
return quickSelect(arr, left, pivot_idx-1, k)
else:
return quickSelect(arr, pivot_idx+1, right, k)
n = len(nums)
return quickSelect(nums, 0, n-1, n-k)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# Hoare Partition
def findKthLargest(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
def partition(arr, left, right):
pivot = arr[right]
i, j = left, right
while True:
while arr[i] < pivot:
i += 1
while j > 0 and arr[j] >= pivot:
j -= 1
# if two pointers meet
if i >= j:
break
else:
arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
arr[i], arr[right] = arr[right], arr[i]
return i
def quickSelect(arr, left, right, k):
if left == right:
return arr[left]
pivot_idx = partition(arr, left, right)
if k == pivot_idx:
return arr[k]
if k < pivot_idx:
return quickSelect(arr, left, pivot_idx-1, k)
else:
return quickSelect(arr, pivot_idx+1, right, k)
n = len(nums)
return quickSelect(nums, 0, n-1, n-k)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32